3. Private Key Operations¶
After the key is unlocked several operations become available:
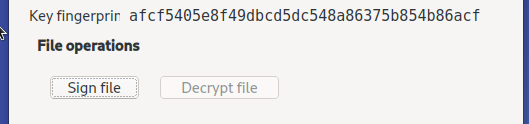
The exact operations that are enabled depend on the key at hand:
if the key is signing capable (one of its component keys have signing key flag set) operations regarding signing data as well as notations are enabled,
if there is an encryption subkey then the decryption operation is enabled,
if the primary key’s secret key is available adding proofs becomes enabled.
Additionally the unlocked key’s fingerprint is displayed for confirmation.
3.1. Sign data¶
Signing data opens a file-picker for a file that needs to be signed and after signing asks for the signed file to be selected.
The operation works regardless if the signing key is a software key or a key on a smart-card.
3.2. Sign notations¶
Signing notations requires certification-capable (primary) key and is used for working with Keyoxide notations.
The exact protocol is described in the Ariadne Id
spec. The operation takes a secret key
and a file describing notations that need to be set. The notations
file is a simple key=value file where keys are notation names and
values are notation values.
An example of such a file which claims that the key owner asserts
control over domain.tld domain and nickname nick on domain.tld
IRC server:
proof@ariadne.id=https://domain.tld
proof@ariadne.id=irc://domain.tld/nickname
proof@ariadne.id=https://domain.tld/user
3.3. Decrypting data¶
Decryption works for keys that have unlocked encryption keys. The workflow is similar to signing but reversed: the encrypted file is selected in the first step and then, after successful decryption, the user is asked about the filename to which the result will be saved.